

Top Privacy Risks in Meta Pixel Setup
Learn Meta Pixel privacy risks — data leaks, cross-site tracking, and legal fines — plus fixes: consent controls, domain limits, and audits.
Meta Pixel is a powerful tool for tracking user actions on websites, but it comes with serious privacy risks if not configured properly. Here's what you need to know:
Sensitive Data Exposure: Misconfigured pixels can unintentionally share personal information like email addresses, health conditions, or financial details.
Privacy Law Violations: Improper setups can breach regulations like GDPR, CCPA, or HIPAA, leading to fines and legal issues.
Cross-Platform Tracking: Poorly managed pixels may collect data from unauthorized domains or multiple website pixels, increasing risks.
Real-World Consequences: Companies have faced millions in fines for privacy violations, with high-profile cases in healthcare, finance, and e-commerce.
Key Fixes:
Consent Management: Use tools to ensure tracking only starts after user consent.
Proper Setup: Limit data collection to approved domains and avoid sensitive data in URL parameters.
Regular Audits: Use tools like Meta Pixel Helper to identify and fix issues.
Ignoring these risks can lead to fines, reputational damage, and loss of trust. Stay compliant by prioritizing user privacy and following best practices.
Stop Tracking Sensitive Data! Fix Meta Pixel & CAPI parameters for MEDICAL Content on WordPress
Common Privacy Risks in Meta Pixel Setup
Meta Pixel Privacy Risks and Features Comparison
After understanding why privacy risks are so critical, let’s dive into the specific ways Meta Pixel configurations can go wrong.
Collecting Sensitive Data Without Permission
Meta Pixel can unintentionally capture sensitive information. For example, URL parameters can expose personal details, like in this scenario: yoursite.com/checkout?email=user@example.com&refund=500. Here, an email address and a refund amount are transmitted directly.
Another concern arises with Automatic Advanced Matching, which scans website forms for personal identifiers such as email addresses and phone numbers, linking them to Facebook profiles. Even when this feature is turned off, the pixel may still pick up form field names like email, address, or phone. Additionally, Automatic Configuration can track button clicks and extract Schema.org metadata without requiring explicit setup.
There have been real-world cases highlighting these risks. For instance, Ramsey Solutions discovered that its pixel was collecting tax-related information, including refund amounts, leading to its immediate deactivation. Similarly, the U.S. Department of Education had to adjust its pixel settings after reports revealed it was capturing the identities of individuals applying for financial aid through FAFSA.
Violating Privacy Laws
Improperly configured Meta Pixels can easily run afoul of privacy regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA, particularly in sensitive industries like healthcare and finance. To address these concerns, Meta has started proactively flagging and blocking custom conversions that might involve sensitive data. For example, starting September 2, 2025, Meta will block data related to health conditions (e.g., "diabetes") or financial metrics (e.g., "credit score"). If such data is detected, Meta will notify you, giving you the opportunity to review your URL parameters and custom events to ensure compliance.
Tracking Users Across Platforms
Meta Pixel’s ability to track user activity across multiple websites and devices can sometimes bypass browser privacy settings. If Traffic Permissions in Events Manager aren’t configured correctly, your pixel might collect data from unauthorized or unfamiliar domains, leading to unintended data collection.
Another challenge arises when multiple pixels are deployed on the same page. Using the fbq('track') function triggers all initialized pixels, potentially causing data to be shared unintentionally. To avoid this, you can use fbq('trackSingle', 'PIXEL_ID', 'EventName'), which ensures the event is sent to a specific pixel only.
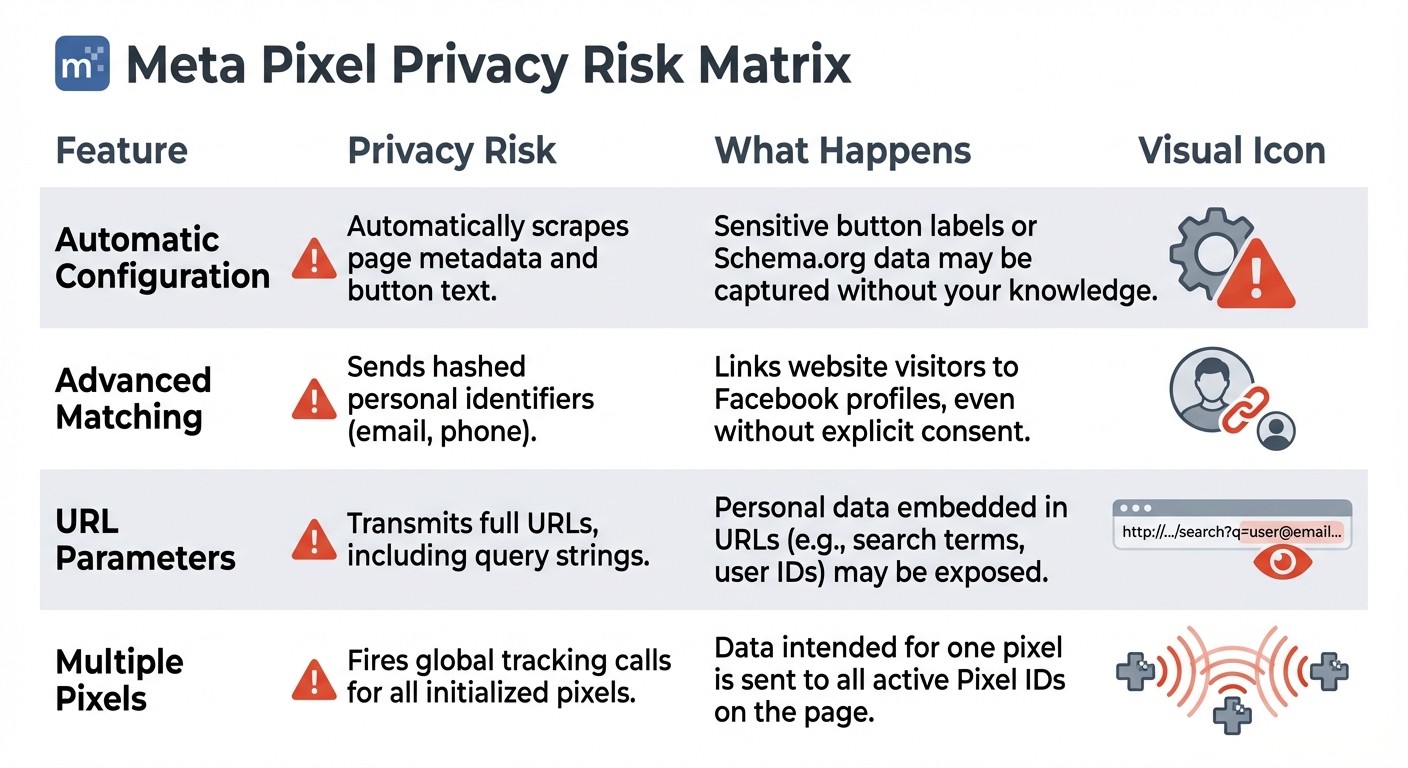
Feature | Privacy Risk | What Happens |
|---|---|---|
Automatic Configuration | Automatically scrapes page metadata and button text | Sensitive button labels or Schema.org data may be captured without your knowledge |
Advanced Matching | Sends hashed personal identifiers (email, phone) | Links website visitors to Facebook profiles, even without explicit consent |
URL Parameters | Transmits full URLs, including query strings | Personal data embedded in URLs (e.g., search terms, user IDs) may be exposed |
Multiple Pixels | Fires global tracking calls for all initialized pixels | Data intended for one pixel is sent to all active Pixel IDs on the page |
Up next, we’ll look at practical steps to address and minimize these privacy risks.
How to Fix Privacy Risks
Now that we've covered the risks, let’s dive into how you can protect both your business and your users.
Use Consent Management Tools
The first step in safeguarding privacy is ensuring the Meta Pixel doesn’t fire until users explicitly give their consent. A Consent Management Platform (CMP) acts as a gatekeeper between your website and the pixel, blocking any tracking until the user clicks "Accept". Importantly, the CMP must provide a "Reject All" button that’s as visible and easy to use as the "Accept All" option. Users should also be able to customize their consent - for instance, they might allow essential website functions but block marketing-related tracking.
Your CMP should automatically recognize and honor Global Privacy Control (GPC) signals and "Do Not Sell/Share" requests to comply with regulations like CCPA and CPRA. Additionally, maintaining consent records is crucial for audit purposes.
Once your CMP is in place, fine-tune your Meta Pixel settings to ensure data collection is limited to approved domains only.
Set Up Meta Pixel Correctly
Using Meta’s Events Manager, set up Traffic Permissions to create an "allow list" of approved domains. This ensures that data is only collected from authorized sources, blocking any unauthorized domains.
Enable the Limited Data Use (LDU) flag to restrict data processing in jurisdictions with stricter privacy laws. To confirm the LDU flag is functioning properly, install the Meta Pixel Helper Chrome extension. This tool will help you verify that data processing parameters like DPOST and DPOCO are being sent correctly. Additionally, make it a habit to audit your URL parameters and test Meta Pixel events. This step ensures sensitive information, such as email addresses, isn’t accidentally included in query strings.
Finally, regular audits are key to identifying and fixing any lingering privacy issues.
Run Regular Privacy Checks
Schedule routine checks of your pixel setup to stay ahead of potential privacy gaps. Use your browser’s developer tools to inspect Facebook-related requests in the Network tab. Look for the ev: field for event names and check udff patterns to ensure personal data isn’t being transmitted. If the is_unavailable field returns true in Events Manager, you’ll need to replace the flagged custom conversion.
If you receive notifications about potential issues, review your URL parameters and custom events right away. Also, use the Meta Pixel Helper extension to confirm the pixel is loading correctly on every page. This tool can also help you catch technical errors, such as invalid IDs or improperly encoded characters.
Here’s a quick summary of tools and methods to help you stay compliant:
Step | Tool/Method | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
Domain Verification | Events Manager Traffic Permissions | Ensure only authorized domains send data |
Payload Inspection | Browser DevTools (Network Tab) | Check for personal information in |
Implementation Check | Meta Pixel Helper Extension | Verify pixel loads correctly and identify errors |
Compliance Review | Events Manager Diagnostics | Address prohibited information notifications |
Consent Check | Consent Management Platform | Confirm pixel only fires after user consent |
Legal and Financial Penalties for Privacy Violations
Privacy violations involving Meta Pixel aren't just hypothetical - they come with hefty financial consequences. From 2023 to 2025, U.S. healthcare providers alone shelled out over $100 million in penalties for unauthorized data sharing through tracking pixels. These penalties go beyond initial fines, often including costs for forensic investigations, user notifications, legal battles, and the damage to a company's reputation.
Real Lawsuits and Settlement Costs
The financial toll of privacy violations is evident in several high-profile cases. In 2024, Mass General Brigham agreed to an $18.4 million settlement over allegations that cookies and pixels on its websites tracked user activity without proper authorization. That same year, Advocate Aurora Health settled for $12.25 million after exposing the data of 3 million patients to Meta due to improper pixel use on its websites and patient portals.
In 2023, BetterHelp, a telehealth platform, paid $7.8 million to the FTC for sharing sensitive mental health data with Meta and other platforms, despite assuring users their information would remain confidential. Similarly, Cerebral settled for $7 million in 2024 for comparable violations. These examples illustrate the steep financial and reputational costs tied to non-compliance with privacy regulations.
"The $5 billion penalty and sweeping conduct relief are unprecedented in the history of the FTC. The relief is designed not only to punish future violations but, more importantly, to change Facebook's entire privacy culture." - Joe Simons, Chairman, Federal Trade Commission
Governments and regulators are stepping up enforcement. Under GDPR, businesses can face fines of up to €20 million or 4% of their global annual revenue, whichever is greater. In 2023, Meta was fined €1.2 billion for unlawful EU–U.S. data transfers and another €390 million for failing to obtain explicit ad consent. California's CCPA imposes penalties ranging from $2,500 per unintentional violation to $7,500 for intentional violations or those involving minors. In 2025, Swedish pharmacies were fined €15 million for improper use of Meta Pixel.
Understanding why use Meta Pixel is essential for balancing marketing goals with these compliance requirements. Next, let's look at how specific industries face unique challenges that amplify these risks.
Risks by Industry
Different industries face distinct legal challenges when their Meta Pixel configurations fail to safeguard user data.
Healthcare and telehealth sectors are under the most scrutiny. A study revealed that 49 out of 50 telehealth websites shared sensitive health data via trackers like Meta Pixel. Following notifications, 35 out of 40 hospitals and health systems removed the tracker from their sites. The risk is particularly serious because the pixel often captures Protected Health Information (PHI) - such as prescription details and addiction survey responses - without a HIPAA-compliant Business Associate Agreement (BAA).
Financial services and tax preparation companies also face exposure. Starting September 2, 2025, Meta began restricting custom conversions that indicate sensitive financial or health conditions, such as "high income" or "diabetes".
E-commerce platforms need to ensure that pixels don't leak personally identifiable information (PII) through advanced matching features. Similarly, educational institutions handling FAFSA applications risk exposing sensitive student financial data.
Industry | Primary Risk | Example Violation |
|---|---|---|
Healthcare | PHI exposure without BAA | Prescription data, addiction survey answers |
Financial Services | Tax and credit data leakage | Refund amounts, credit scores |
E-commerce | PII exposure through advanced matching | Leakage of personal data via pixel matching |
Education | Exposure of financial aid and student records | Sensitive financial aid data |
Conclusion
Key Points to Remember
Meta Pixel comes with privacy risks that can be both serious and expensive. These risks include unauthorized data collection, capturing sensitive information like health or financial details, and failing to meet privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. Ignoring these issues can result in hefty financial penalties.
To maintain compliance, it's crucial to take a proactive approach. Make sure consent management systems block pixel activation until users explicitly opt in. Limit data collection to only what's necessary for your events, and conduct regular audits using tools like Meta Pixel Helper to ensure no prohibited data is being captured. Also, your privacy policies should clearly explain what data is collected and who it’s shared with.
Adopting these measures can help you avoid costly mistakes and stay aligned with privacy standards.
Tools That Help with Compliance
Managing compliance manually while running multiple ad campaigns can quickly become overwhelming. Balancing performance goals with privacy requirements is no easy task. That’s where tools like AdAmigo.ai come in. This platform automates Meta ad management, optimizing campaigns based on your goals while adhering to budget, pacing, geo, and placement guidelines.
AdAmigo.ai’s AI Ads Agent analyzes your brand to identify top-performing ads and delivers fully configured creatives straight into your ad account. For businesses and agencies juggling heavy workloads, the platform’s daily AI Actions provide a prioritized list of impactful adjustments across creatives, audiences, budgets, and bids. Whether you prefer a fully autonomous setup or one with approval steps, this tool simplifies campaign management, allowing you to focus on strategy and ensuring compliance.
FAQs
How can businesses make sure their Meta Pixel setup complies with privacy laws?
To keep your Meta Pixel setup in line with privacy regulations, start by reviewing Meta’s Business Tools Terms, Data Processing, and Data Security agreements. Align these requirements with your privacy policy and the laws relevant to your audience, such as GDPR or CCPA. Collect only the data you need for measurement or targeting, and avoid sending personally identifiable information (like full names or email addresses) unless you have explicit user consent.
Set up your pixel with privacy-focused configurations. In Events Manager, use traffic permissions to ensure only approved domains can send events, blocking any unknown sources. Pair the pixel with the Conversions API to handle server-side data securely - filtering, encrypting, and matching it to user consent before sending it to Meta. Test your setup using the Meta Pixel Helper tool to confirm that only the intended events are tracked and no sensitive data is shared.
Make sure your site includes a transparent consent mechanism, such as a clear cookie banner that explains the pixel’s purpose and data collection practices. Give users the option to opt in or out before any tracking occurs, and keep records of their preferences. Regularly audit your pixel setup to ensure it complies with changing privacy laws and Meta’s guidelines.
What happens if the Meta Pixel is set up incorrectly?
Incorrectly setting up the Meta Pixel can expose you to significant privacy risks. If too much or sensitive user data is shared, it could violate privacy laws and lead to legal trouble. On top of that, a misconfigured Pixel can throw off your ad performance. You might face inaccurate conversion tracking, weak audience targeting, and flawed reporting - all of which can drain your ad budget and hurt the success of your campaigns.
To steer clear of these problems, make sure your Pixel is set up correctly. Focus on following privacy regulations and collecting only the data you need to fine-tune your ad strategy. This way, you can stay compliant while maximizing your campaign’s potential.
What privacy risks come with using Meta Pixel for tracking across platforms?
Using Meta Pixel for tracking across platforms can raise privacy concerns. It gathers data such as IP addresses, browser information, cookies, and user behaviors across websites, apps, and partner platforms. This information is used to build detailed user profiles that stretch beyond a single site and can be shared with Meta or even third parties for targeted advertising.
The main risks involve the potential for over-collection or accidental exposure of sensitive user data, particularly when consent mechanisms aren't uniformly applied across platforms. These practices could also conflict with privacy regulations like GDPR, CCPA, or HIPAA, potentially resulting in legal consequences. The broader the tracking network, the greater the likelihood of privacy violations and compliance challenges.