Price increase Feb 3: $350. Start your trial now to lock in current pricing.
Meta’s AI tools, like Advantage+ and Meta Lattice, promise to make ad management effortless by automating tasks like targeting, creative generation, and budget optimization. Advertisers can now set a goal, and AI handles the rest. These tools improve ad performance, with reported increases in conversion rates and return on ad spend. However, this efficiency comes at a cost: user privacy.
Meta uses data from over 1 billion monthly chatbot interactions across platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp to personalize ads without privacy risks. Users unknowingly share sensitive details, believing their conversations are private. Critics argue that this practice, combined with limited opt-out options, erodes trust. Automated privacy reviews replace human oversight, raising concerns about ethical risks and regulatory compliance.
For advertisers, balancing AI’s performance benefits with privacy concerns is critical. Tools like AdAmigo.ai offer an alternative by optimizing campaigns without mining personal conversations, ensuring greater control over data use. As privacy laws tighten, transparency and ethical data practices will define the future of AI-driven advertising.
Controversial Meta Privacy Policy Update
Beyond platform-wide policy shifts, advertisers must also consider how vendor security breaches can compromise sensitive campaign data.
Benefits of Meta Ads AI
Manual vs AI-Driven Ad Management: Key Differences
Despite ongoing privacy concerns, Meta's AI tools have gained traction by delivering measurable performance improvements. Through advanced systems like Meta Lattice and GEM, the company has streamlined ad placements across Feed, Stories, and Reels, reducing the need for manual intervention and boosting key advertising metrics.
Better Ad Performance Through Automation
Meta's AI takes over tasks that used to demand significant manual effort. Tools like Advantage+ simplify audience discovery, ad placement, and bidding, while the AI Sandbox generates and tests various creative options. These systems analyze raw user behavior through event-based features (EBFs), uncovering intent signals that traditional demographic targeting might overlook. They also tackle common challenges like delayed feedback and the "cold start" problem for new campaigns.
Avi Ben-Zvi, VP of Paid Social at Tinuiti, highlighted the impact of these advancements:
"It's basically taking the legwork out. It's been a general boost towards efficiency".
Automation also extends into creative production, where AI leverages brand identity and competitive trends to craft effective ads. This automation doesn’t just improve performance - it saves time and reduces costs.
Time and Cost Savings
The time saved by automation translates into direct cost reductions. Agencies using AI-driven tools report that a single media buyer can manage four to eight times more clients by automating repetitive tasks. This shift allows experienced staff to focus on strategy rather than routine campaign management. For small and medium-sized businesses, AI provides an affordable alternative to expensive agency retainers, leveling the playing field for those with limited marketing budgets.
Meta is moving toward a fully automated advertising model, where advertisers simply set a budget and objective, and AI takes over everything - from generating creatives to optimizing media placements. Alex Schultz, Meta's CMO and VP of Analytics, explained:
"AI will enable agencies and advertisers to focus precious time and resources on the creativity that matters".
This shift highlights the stark contrast between manual and AI-driven ad management approaches.
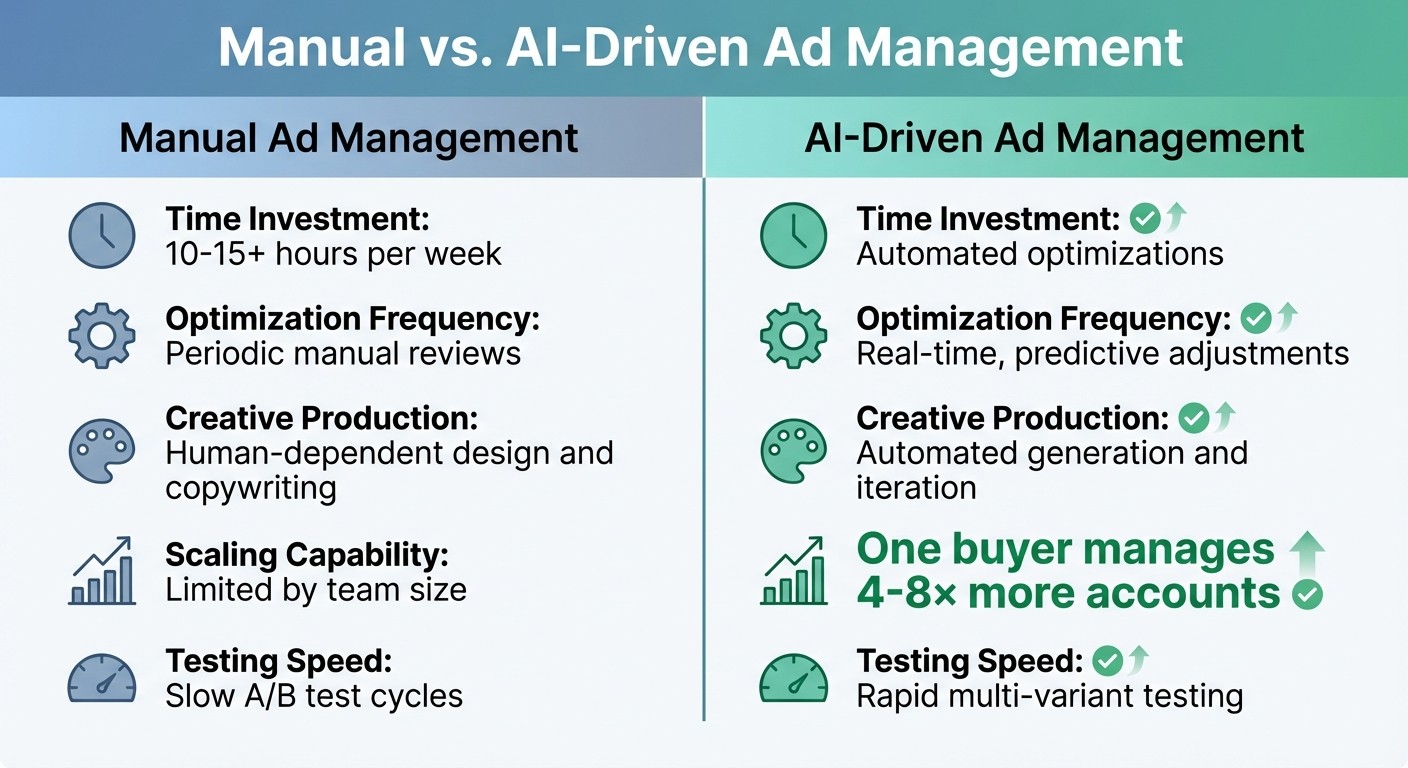
Manual vs. AI-Driven Ad Management
The differences between traditional and AI-powered ad management are striking:
Feature | Manual Ad Management | AI-Driven Ad Management |
|---|---|---|
Time Investment | 10–15+ hours per week | Automated optimizations |
Optimization Frequency | Periodic manual reviews | Real-time, predictive adjustments |
Creative Production | Human-dependent design and copywriting | Automated generation and iteration |
Scaling Capability | Limited by team size | One buyer manages 4–8× more accounts |
Testing Speed | Slow A/B test cycles |
Platforms like AdAmigo.ai take these efficiencies even further by integrating creative generation, targeting, and budget optimization into a single tool. Its AI Ads Agent analyzes brand identity and competitor performance to produce complete ad creatives with just one click. Meanwhile, its AI Actions feature provides a daily list of prioritized tweaks, automating execution while leaving strategic decisions to human experts. This allows media buyers to handle more accounts without sacrificing results.
While the performance benefits of AI-driven advertising are undeniable, ensuring these advancements align with strong privacy protections remains essential.
Privacy Risks of Meta Ads AI
While Meta's AI has proven effective in optimizing ads, its reliance on extensive data collection raises serious privacy concerns. Critics argue that Meta's approach to gathering and using personal information often leaves users feeling powerless over how their data fuels advertising algorithms. This has drawn scrutiny from regulators, privacy advocates, and users alike.
How Meta Collects User Data
Meta's AI gathers data from a variety of sources across its platforms, including Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, and Messenger. For example, it mines chatbot conversations - text, images, and prompts - to create detailed ad profiles. The company also collects data through hardware, such as its Ray-Ban smart glasses, which capture voice recordings, photos, and videos to refine ad targeting with AI tools. With over 1 billion monthly active users engaging with Meta AI features as of late 2025, the scale of conversational data available for ad targeting has grown dramatically.
To manage this massive influx of data, Meta has shifted toward automated risk assessments, using AI to handle up to 90% of its privacy and safety reviews. However, this reliance on automation has raised alarms. A former Meta executive cautioned:
"Insofar as this process functionally means more stuff launching faster, with less rigorous scrutiny and opposition, it means you're creating higher risks."
Another area of concern is the use of proxy audiences, where AI infers sensitive traits based on related conversations. Although Meta claims it does not target ads based on health conditions or religious views, discussions around topics like "World Diabetes Day" could unintentionally signal personal health information. These practices highlight the ethical and legal dilemmas that come with such aggressive data collection.
Legal and Ethical Issues
Meta's data practices have not only sparked ethical debates but have also led to regulatory action. In 2019, the Federal Trade Commission fined Meta $5 billion for privacy and advertising violations. More recently, in October 2025, a Dutch court ruled under the EU Digital Services Act that Meta must provide users with the option to view chronological feeds instead of algorithm-driven ones.
The ethical issues extend beyond compliance with regulations. Users often share sensitive information under the assumption of privacy, only to find it monetized without their explicit consent. For instance, in October 2025, a coalition of 36 privacy and civil rights organizations urged the FTC to investigate Meta’s decision to use chatbot interactions for advertising purposes without offering an opt-out option. The financial incentives tied to linking chatbot data with ad revenue push Meta to encourage deeper user engagement, further increasing data collection.
These legal and ethical challenges exacerbate user concerns, underscoring the need for greater transparency and control.
User Control and Transparency
Meta has faced criticism for failing to meet user expectations around transparency and control. As of December 16, 2025, users in the United States cannot opt out of having their data used for AI purposes. Their only option is to avoid AI features altogether. In contrast, stricter laws in the EU, UK, and South Korea provide users in those regions with additional protections. Notifications about data use are often unclear and require navigating multiple screens to understand how AI conversations are leveraged for advertising.
A glaring example of Meta's transparency shortcomings occurred in June 2025, when a "share" feature caused private chatbot prompts - some involving gender identity and medical concerns - to be published under users' real names. This privacy lapse, reported by TechCrunch, highlighted the risks of confusing and poorly designed features.
Privacy Feature | US Users | EU/UK/South Korea Users |
|---|---|---|
Opt-out from AI data use | Not available | Protected by DSA and local laws |
Chronological feed option | Not required | Mandated by court ruling |
AI chat data for ads | Mandatory (unless you avoid AI) | Subject to regional restrictions |
These issues reveal a significant disconnect between Meta's claims about transparency and the actual level of user control. As AI continues to dominate the advertising landscape, the need for clearer policies and better safeguards becomes increasingly urgent.
Finding the Balance Between AI and Privacy
Meta's advanced AI tools bring both opportunities and challenges, particularly when it comes to balancing performance with privacy. To navigate this, advertisers need to actively manage these tools while staying informed about how data flows through the system.
Meta's Advantage+ tools have been a lifeline for many advertisers trying to recover from the impact of Apple's 2021 privacy updates. That said, these automated systems operate with limited transparency, leaving advertisers in the dark about how their data - and their customers' data - is being used. Reports suggest a 10%–15% drop in performance compared to pre-ATT levels. This raises concerns that customer data might inadvertently end up training competitors' models. Conducting regular audits of data flows is essential to ensure compliance with internal privacy standards. This highlights the ongoing challenge of achieving strong campaign performance without compromising on data privacy.
AdAmigo.ai: AI That Prioritizes Privacy
AdAmigo.ai takes a different approach by working strictly within the boundaries set by advertisers. This autonomous AI agent optimizes creative assets, targeting, and budgets while adhering to all campaign-specific rules.
Unlike some tools, AdAmigo.ai doesn’t mine user chats or conversations for ad signals. Instead, it focuses solely on the campaign data and brand guidelines provided by advertisers, using actual ad performance to refine results over time. Advertisers can choose to let it operate autonomously or review and approve actions manually. This level of control stands in contrast to Meta's Advantage+ tools, which are often criticized for their lack of transparency.
Feature | Meta Native AI (Advantage+) | AdAmigo.ai |
|---|---|---|
Data Sources | User chats and cross-app activity | Campaign performance data and brand inputs only |
Advertiser Control | Limited; operates as a "black box" | Full transparency; approve or auto-publish each action |
Privacy Compliance | Automates 90% of internal risk assessments | Respects all advertiser-set geo, budget, and placement rules |
Customer Data Sharing | May train models used by competitors | Learning limited to your campaign |
User Opt-Out | Not available for U.S. users | N/A - does not access user chat or behavioral data |
AdAmigo.ai enables a single media buyer to manage up to eight times more accounts, offering in-house teams an efficient, privacy-safe way to run campaigns.
Reducing Privacy Risks in Advertising
Selecting a privacy-conscious AI tool is just the first step - advertisers must also stay proactive about managing their data practices. Regularly audit your data flows to ensure compliance with internal privacy policies. If your campaigns target EU audiences, take advantage of Meta's Ireland-based oversight, which enforces stricter protections under the Digital Services Act and GDPR.
Be cautious of "proxy audiences." While Meta claims its AI filters out sensitive topics like health conditions, religious beliefs, and sexual orientation, the system may still infer these traits indirectly. For instance, mentioning "World Diabetes Day" might signal a connection to a health condition without explicitly stating it. Keep a close eye on your audience targeting to avoid unintentionally reaching users based on inferred sensitive characteristics.
Finally, compare the results of manual campaigns with those run by AI-driven tools using Meta's measurement reports. Automation doesn’t always guarantee better ROI. Solutions like AdAmigo.ai offer the efficiency of AI while providing the transparency and control needed to align your campaigns with both your privacy standards and business objectives.
Conclusion: Managing AI Performance and Privacy
AI-driven Meta ads streamline tasks like creative testing, audience targeting, and budget management. But there's a catch: the same data that enhances targeting also raises privacy concerns. For instance, Meta uses AI chatbot conversations to gather ad signals, and U.S. users currently have no option to opt out. Overlooking these privacy concerns can erode the trust that makes personalized ads effective.
"The foundation of Meta's AI goals is a business model that requires users to voluntarily share data. Customers may reduce engagement... if they believe that default settings and ambiguous controls are misleading." – Jeremy Goldman, Analyst, EMARKETER
To succeed in the long run, businesses need to merge automation with accountability. This means auditing how data is handled, adhering to privacy regulations, and offering transparent tools. While Meta's Advantage+ tools can help recover some of the 10%–15% performance loss caused by Apple's privacy updates, they leave advertisers in the dark about how customer data is actually being used. Striking a balance between efficiency and transparency is crucial.
Unlike systems such as Advantage+, a hybrid approach offers the best of both worlds. AI can handle optimization, while humans retain control over strategy in manual vs AI-powered management models, creative decisions, and ethical data use. Platforms like AdAmigo.ai demonstrate that automation doesn’t have to mean losing oversight. Advertisers can choose to approve every action or let campaigns run automatically, with data usage strictly tied to campaign performance - not private conversations.
Performance and privacy don’t have to be at odds. Businesses that prioritize both will not only foster stronger customer relationships but also stay ahead of regulatory changes and avoid the backlash that comes from treating personalization like surveillance. By balancing these priorities, companies can build a more sustainable and trustworthy advertising model.
FAQs
How does Meta's AI improve ad performance while addressing privacy concerns?
Meta is leveraging AI to boost ad performance by analyzing user interactions - like chat prompts and metadata - to refine creatives, target audiences, and optimize bids and budgets. This data-driven strategy enables advertisers to craft more relevant campaigns and achieve better returns on ad spend (ROAS). Similarly, platforms like AdAmigo.ai use AI to experiment with creative variations, fine-tune targeting, and manage budgets within user-defined constraints.
On the flip side, privacy advocates have raised alarms about how Meta handles user data. According to its privacy policy, Meta collects and utilizes AI chat content, including messages and media, to personalize ads. Critics argue this mandatory data collection lacks transparency and doesn’t offer users the ability to opt out, which could pose risks to personal privacy. While Meta’s AI-driven approach enhances ad relevance, the tension between improved performance and safeguarding user privacy remains a pressing issue.
What privacy concerns arise from Meta's use of AI for ad targeting?
Meta's ad system, powered by AI, taps into data from users' interactions with its generative AI tools - including private conversations - to fine-tune ad targeting. This means that even personal details, like opinions or sensitive information shared in chats, can be used to craft detailed advertising profiles. And here's the catch: there's no way for users to opt out.
This approach has sparked serious privacy concerns. By allowing advertisers to deduce intimate aspects of users' lives, it raises red flags about potential violations of personal boundaries. Critics emphasize that the absence of opt-out options for U.S. users weakens privacy safeguards and heightens the risk of data misuse or manipulation. Without giving users control, this system could pave the way for unwanted profiling and the exposure of private information.
How can advertisers use AI tools for Meta ads while staying compliant with privacy laws?
Advertisers can successfully navigate the tricky balance between AI-driven ad optimization and privacy laws by sticking to a few smart practices. Start by securing clear, informed consent from users before collecting or using their data for AI purposes. This is especially important given Meta's updated policies, which now classify interactions like chats and metadata as ad-relevant information.
Next, adopt privacy-by-design measures to protect user data. This might include anonymizing or aggregating data, setting strict limits on how long data is retained, and clearly documenting the purpose and legal basis for every instance of data use.
It's also crucial to offer users a transparent opt-out option or access to a privacy dashboard. This step helps meet the requirements of regulations like GDPR and CCPA. On top of that, regularly audit your AI models and data pipelines to ensure they aren’t unintentionally revealing sensitive information or re-identifying individuals.
Lastly, keep thorough records of user consent, data handling procedures, and any third-party AI tools you use. These records can be invaluable for demonstrating compliance if questions arise. By focusing on transparency, user consent, and strong privacy safeguards, advertisers can take advantage of AI’s potential without running afoul of privacy laws.
